1 reselection
Gravity separation method is to separate minerals according to the difference of mineral relative density (usually called specific gravity). Mineral particles with different densities are subjected to hydrodynamic and various mechanical forces in moving media (water, air and heavy liquid), resulting in suitable loose stratification and separation conditions, so that mineral particles with different densities can be separated.
Gravity election is one of the common methods of gold election. In placer gold deposits, gold usually exists in the form of monomer natural gold, and the particle size is generally greater than 16 tons / m3, which is greatly different from the density of gangue. Therefore, gravity separation is the main, effective and economic method to separate placer gold deposits. However, in pulse gold, gravity separation is rarely used alone and is not a part of the combined gold extraction process. Generally, jigs, spiral chutes and shakers are used in the grinding and classification circuit to recover the cleaved coarse-grained monomer gold in advance, so as to facilitate the subsequent flotation and hydrogenation operations and obtain qualified gold concentrate. This method is widely used in small gold mines and local group mining, such as Jinchanggouliang, dashuiqing and other gold mines in Inner Mongolia.
The main equipment for gravity separation of gold is various forms of chutes, jigs and shakers. In addition to conventional gravity separation equipment, on the basis of digestion and absorption equipment, new gravity separation equipment such as belt chute, Ross chute, circular jig and placer gold centrifugal washing unit have been developed, which has achieved good results in gold production. Mercury mixing method is widely used in placer gold mines to separate gold and heavy placer minerals; In vein gold mines, mercury is usually mixed with flotation, gravity separation, cyanidation, etc. as part of the combined process, which is mainly used to collect coarse-grained monomer gold.
1) Jigging method
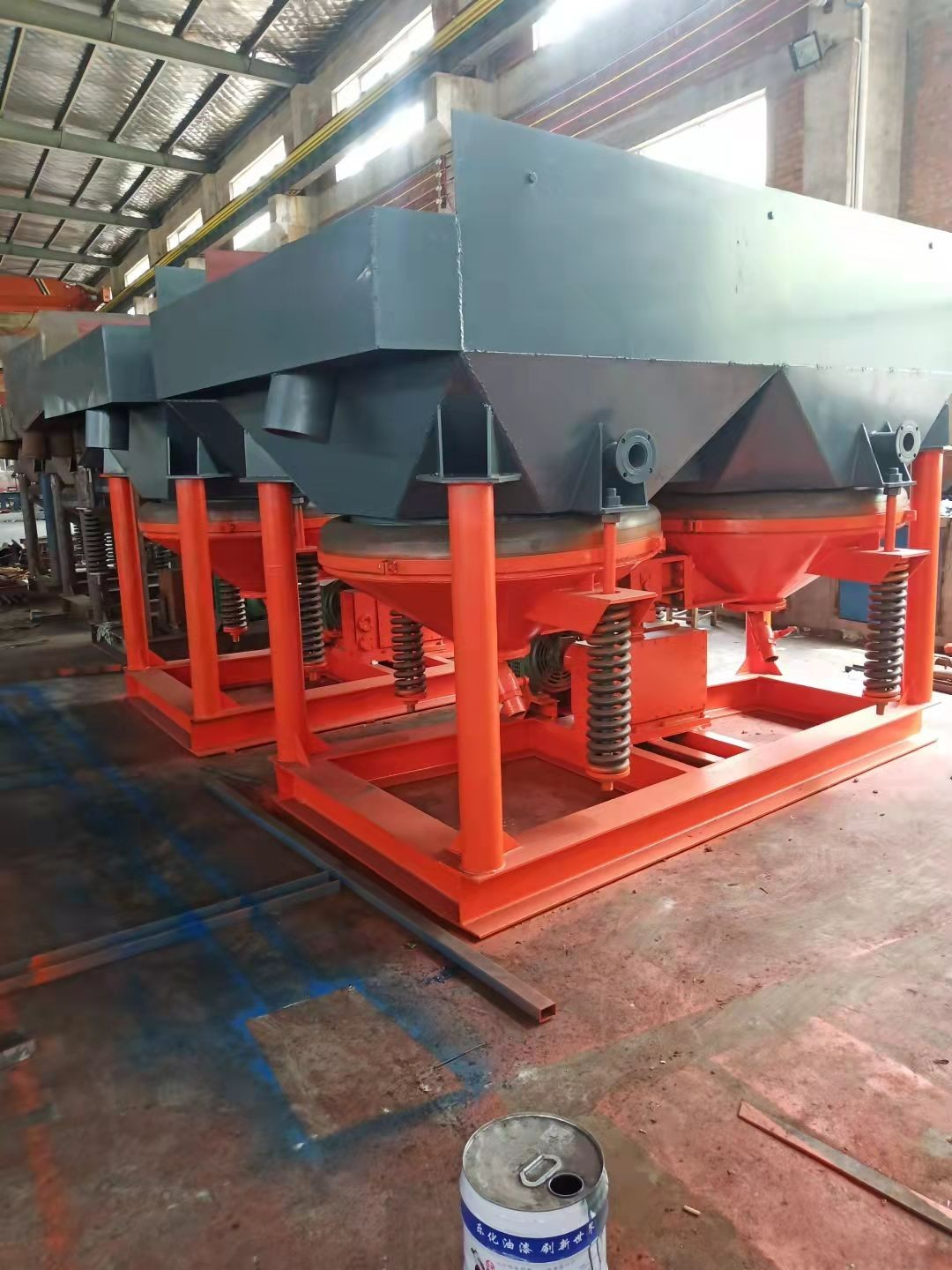
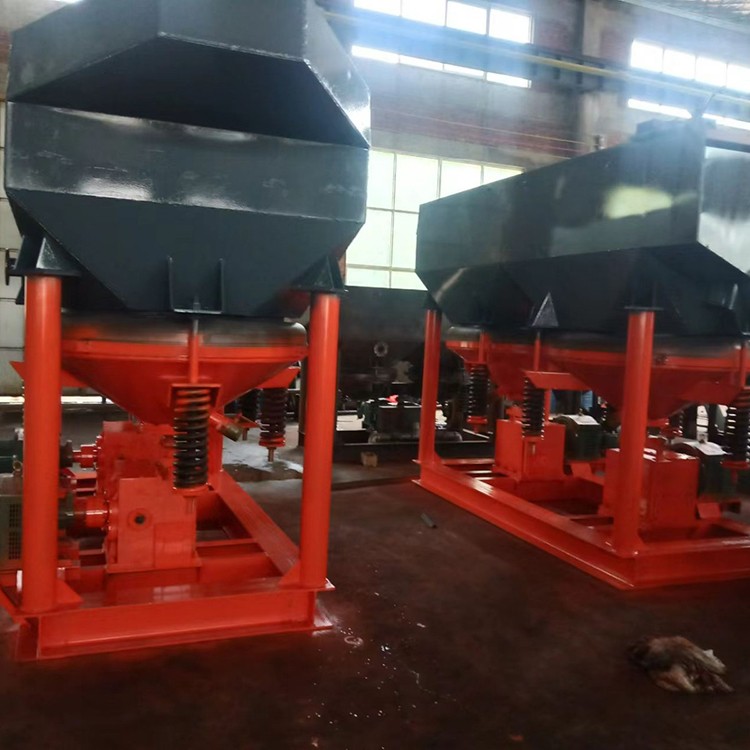
Jigging is a gold separation process with jigging machine as gold separation equipment. Jigs are commonly used gravity separation equipment with many types.
The working principle of the diaphragm jig is: when the eccentric transmission mechanism drives the diaphragm to move back and forth, the water in the jig chamber will pass through the vertical alternating pulsating water flow generated by the screen. The selected materials are fed to the bed and form a particle group system with the bed ore and water. When the water flows upward, the particle group is in a loose suspension state. At this time, mineral particles with different weight and size settle at different speeds, and large-density coarse particles (bed stones) settle in the lower layer. When the water flow drops, there is suction, and the mineral particles with high density and small particle size enter the lower layer through the bed gap.
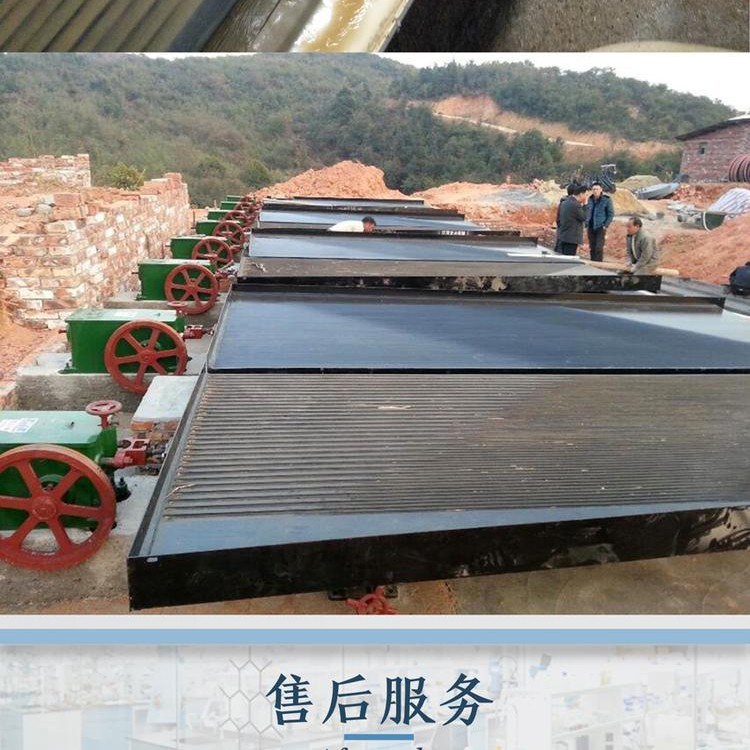
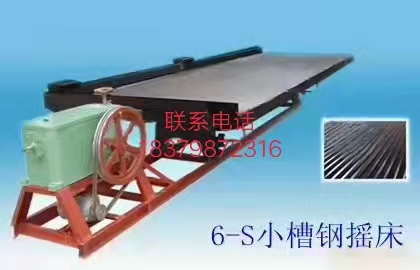
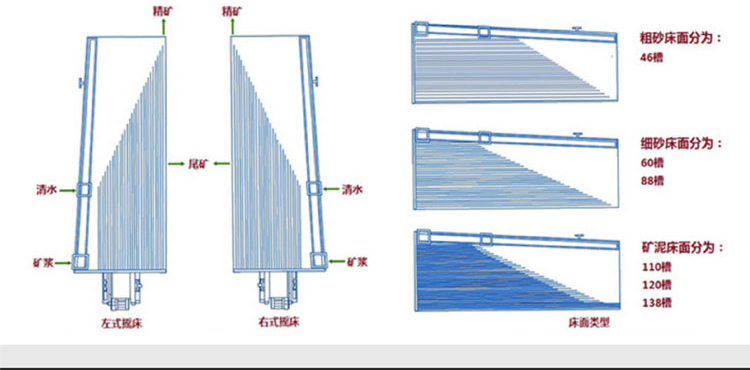
2) Shaking table method
Shaking table gold separation method is a gold separation process with shaking table as the main equipment. Shaking table is a device for beneficiation in horizontal medium flow. It is composed of bed surface and transmission mechanism. The bed surface is driven by the transmission mechanism to move back and forth longitudinally. The separation of ore on the shaking table is gradually completed in the process of reciprocating motion of the bed surface. In addition to its own gravity, the main factors contributing to the movement of ore particles are scouring and bed differential movement. Ore particles undergo stratification perpendicular to the bed surface and separation parallel to the bed surface during movement. The result of the two actions is that different ore particles are discharged from different sections of the bed surface.
Shaking table can be divided into coarse sand bed (>0.5 mm), fine sand bed (0.5 ~ 0.074 mm) and slime bed (0.074 ~ 0.037 mm) according to the different particle sizes of the selected ores.
3) Chute beneficiation
The chute gold separation method is a gravity separation method. The main equipment of chute gold selection is chute. The chute is a long and narrow wooden (or steel) chute with an inclination of 3 ° ~ 4 ° (no more than 14 ° ~ 16 °). The gold industry can be manufactured locally. The separation principle is: after the slurry is fed into the chute from the trough head, under the combined action of water force, ore particle gravity (or centrifugal force), friction between ore particles and the trough bottom, ore particles with different densities are loosely stratified and separated. The higher density becomes concentrate at the trough bottom, and the lower density becomes tailings. The chute is operated intermittently. When the concentrate at the bottom of the chute is deposited to a certain height, stop feeding and clear the concentrate.
The chute is divided into coarse sand chute and slime chute. The former is suitable for handling coarse-grained materials, and the latter is suitable for handling fine-grained materials. Pavements and baffles are installed at the bottom of coarse-grained chute.
Coarse grain chute is the main equipment for gold placer beneficiation, which is used on land and on gold mining ships. The large chute on land is generally about 15 meters, and that on gold mining ships is generally 4 ~ 6 meters.
4) Gold separation by spiral concentrator
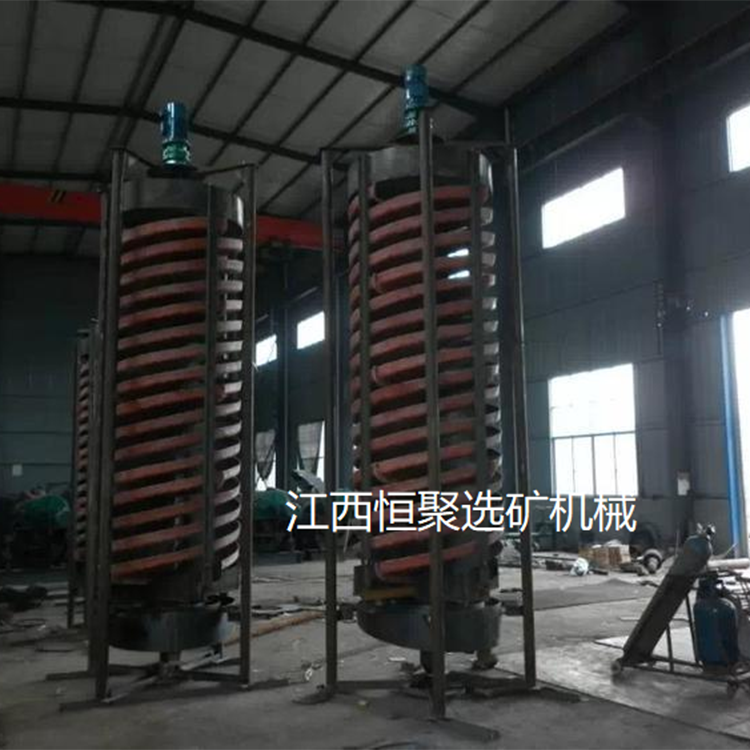
Spiral concentrator gold separation method is a gold separation process with spiral concentrator as the main equipment. The spiral concentrator uses the combined action of gravity, friction, centrifugal force and water flow to make the ore particles A kind of chute beneficiation equipment with shape separation (. The whole chute is bent into a spiral shape in the vertical direction. The sorting process is: the slurry fed from the top of the chute flows downward in a spiral shape along the chute. In the flow process, the ore particles are stratified. Large particles with small density are distributed on the outer edge of the spiral chute, and fine particles with large density are distributed on the inner edge of the spiral chute. The heavy products after stratification are discharged from the discharge port at the bottom of the inner chute with interceptors, and the light products are discharged from the end of the spiral chute Out.
The spiral concentrator is simple in structure, easy to manufacture, without transmission mechanism and power; The effect of selecting materials above 6mm, below 0.05mm and containing flat gangue is poor..
5) Gold separation with cone concentrator
Cone concentrator is evolved from the principle of sharp shrinkage chute (also known as fan-shaped chute). The pinch chute is fan-shaped, about 1 meter long, 125 ~ 400mm wide at the feeding end, 25 ~ 9mm wide at the discharging end, and the chute surface is placed obliquely.
2 mercury mixing method
Mercury mixing method can be divided into internal and external mercury mixing according to its production mode. Mercury mixing method is widely used in placer gold mines to separate gold and heavy placer minerals; In vein gold mines, mercury mixing is usually used as a part of the combined process, combined with flotation, gravity separation, cyanidation, etc., mainly to promote the capture of coarse-grained monomer gold.
Internal mercury mixing is carried out in the mercury mixing cylinder or grinding machine, which can better control mercury pollution.
The main equipment for external mercury mixing is mercury mixing plate, which is composed of support, bed surface and mercury plate. Mercury plate materials are copper plate, silver plated copper plate, mercury plate, etc., and the mercury mixing effect of silver plated copper plate is good. In order to facilitate silver plating and replacement in production, electrolytic copper plates are often cut into small pieces with a width of 400 ~ 600mm and a length of 800 ~ 1200mm. After silver plating, they are laid on the bed surface one by one according to the inclined direction of the support.
The determination of mercury plate area is related to the amount of ore processed, the nature of ore and the role of mercury mixing in the gold separation process. Generally, when the pulp flow depth on the mercury plate is 5 ~ 8mm and the flow rate is 0.5 ~ 0.7 m / s, the mercury plate area required to process a ton of ore is 0.05 ~ 0.5 m2 / T · day. If the mixed mercury is only to collect large particles of free gold, and its tailings still need flotation, gravity separation and cyanidation, the public quota can be set at 0.1 ~ 0.2 square meters / ton / day.

































 The1year
The1year




 Gold mill
Gold mill
 Kazakhstan Shajin gravity separat
Kazakhstan Shajin gravity separat
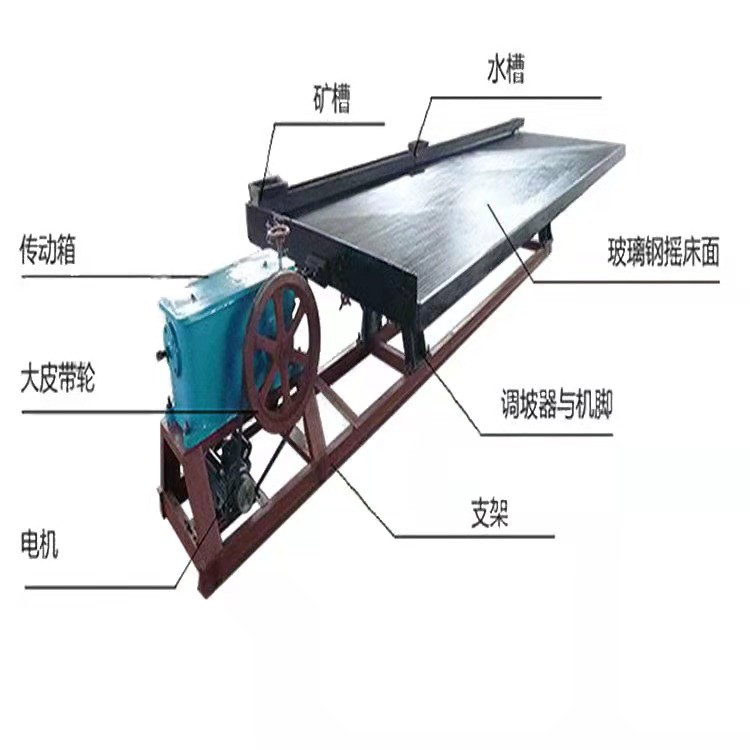 Gold dressing shaker
Gold dressing shaker
 Copper ore, iron ore, placer gold
Copper ore, iron ore, placer gold
 Copper ore, iron ore, placer gold
Copper ore, iron ore, placer gold
 Rare earth tungsten tin ore titan
Rare earth tungsten tin ore titan
 Mobile crusher
Mobile crusher
 Central shaft drive roller screen
Central shaft drive roller screen
 Shajin centrifugal concentrator
Shajin centrifugal concentrator











